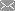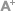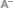Starburst: Chilean Astronomers Photograph Most Spectacular Massive Star Cluster Ever Seen in Our Galaxy
- CH Smith
- Aug 20, 2014 02:17 PM EDT
- Sign up to receive the lastest news from LATINONE
-
The La Silla Observatory in Chile discovered a spectacular star formation in the southern area of the Milky Way. The discovery of the NGC 3603 star cluster is notable because it's known for having the highest collection of massive stars that have ever been seen in our galaxy.
It's a young cluster of stars that was first discovered by an astronomer in South Africa in 1834. At the center of the cluster is the Wolf-Rayet multiple star system, which is called HD 97950. The stars in the Wolf-Rayet region are about 20 times the mass of the sun, since they are in an advanced stage of development, but they lose a lot of their mass through intense stellar winds, according to the ESO.org.
As the European Southern Observatory organization explains, stars come to life in the most dusty, dark regions of space, and way out of view of telescopes. However, as the youngest of the stars begins to slowly shine and break away from their developing materials, the stars are more visible with glowing clouds surrounding them, the website said. These glowing clouds are known as HII regions, and they get their shine from interacting with ultraviolet radiation that's emitted from the younger stars, which are burning with hydrogen gas clouds. These regions can be huge and measure several hundred light-years in diameter, according to the ESO, and the one surrounding NGC 3603 is the most massive region in our galaxy, the group said.
NGC 3603 is 20,000 light years away, and located in the Carina-Sagittarius spiral arm of the Milky Way. Another object astronomers found is called the NGC 3576 and is a collection of glowing gas clouds that are about 9,000 light years away from Earth.
Astronomers say that the thing that makes NGC 3576 unique is it has a curled horn shape, like that of a ram. It takes the shape from the stellar winds that blow through the central regions of the nebula, causing dust and gas to scatter over a hundred light-years.
- Sign up to receive the lastest news from LATINONE
-